
Initial GALILEO services will be made available by the end of 2016. Although the only reliable and extensive GNSS presently available is the GPS coverage of the US Department of Defence, there is also the partially operative Russian Global Orbiting Navigation System (GLONASS) system and the planned European system, GALILEO. RNAV of sufficient accuracy is now seen ultimately as providing a replacement for all ground-based navigational aids. The advent of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), mainly in the specific form of GPS, has now brought a completely new opportunity to derive an accurate three-dimensional (VNAV) position as well as a highly accurate two-dimensional (LNAV) position over an area not restricted by the disposition of ground transmitters. As RNAV accuracy has improved, it has begun to play a vital role in increasing ATM efficiency whilst also sustaining safety performance. LORAN ‘C’ can also be used in certain circumstances and lNS can be used to maintain prior tracking for up to 2 hours. More recently R-NAV moved to position derived from VHF Omnidirectional Radio Range (VOR) radials (up to 62nm slant distance) and/or Distance Measuring Equipment (DME) distances. Various types of ground-based area navigation systems have been available from terrestrial sources for nearly thirty years these were originally dependent on VLF/Omega and LORAN ‘C’ long range radio signals. RNAV includes Performance Based Navigation (PBN) as well as other RNAV operations that are not within the definition of PBN. The back of the E6B is used to find ground speed and determine how much wind correction you need.RNAV is a method of navigation which permits the operation of an aircraft on any desired flight path it allows its position to be continuously determined wherever it is rather than only along tracks between individual ground navigation aids.

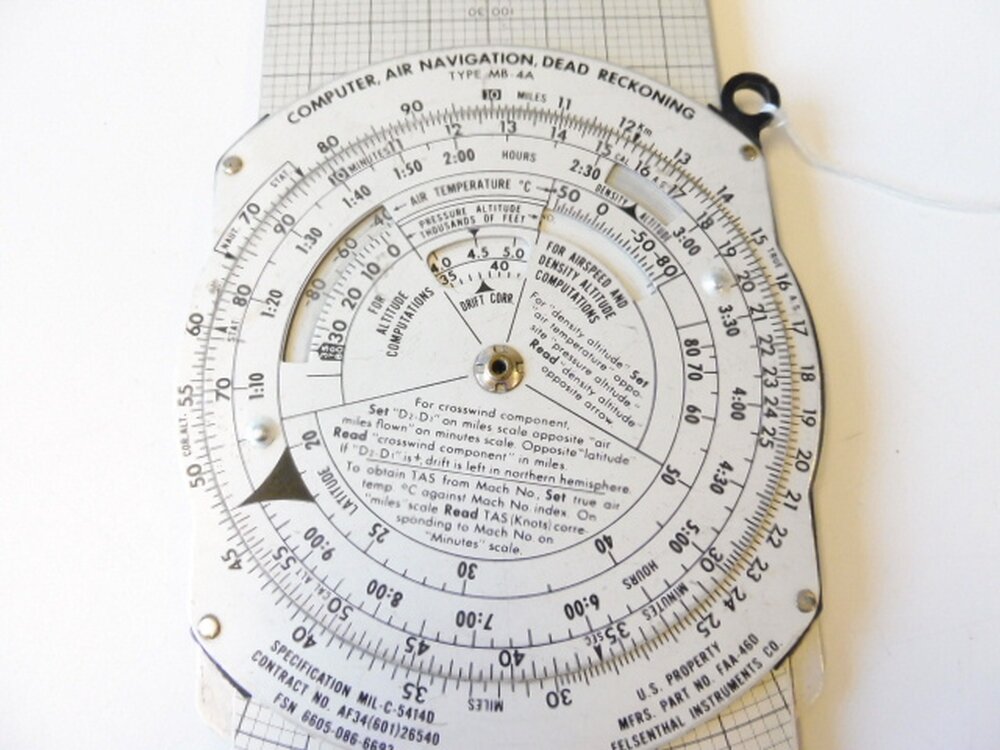
On either side of the front you will have rulers, one for statute miles and one for nautical miles on your sectional map.Īnother very useful part is the conversion scale on the front outer circle, which helps convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius. Below that you will find a grid called crosswind correction, this grid shows you the difference you need to correct for because of wind. The crosswind component is the amount of crosswind in knots that is being applied to the airframe and can be less than the actual speed of the wind because of the angle. On the main body of the flight computer you will find the wind component grid, which you will use to find how much crosswind you will actually have to correct for. This can also be done backwards to find the amount of time it will take to travel a given number of nautical miles. Looking at the inner ring for minutes traveled and the distance traveled will be above it on the outer ring. 60 is used in reference to the number of minutes in an hour, by placing the 60 on the airspeed in knots, on the outer ring you can find how far you will travel in any given number of minutes. Take the number 60 on the inner circle which usually has an arrow, and sometimes says rate on it. One of the most useful parts of the E6B, is the technique of finding distance over time.
#COMPUTER AIR NAVIGATION HOW TO#
(Electronic option is available and can be used on FAA exams but pilots are still expected to know how to use the analog version.) The back is designed for wind correction calculations, i.e., determining how much the wind is affecting one's speed and course. In the air, the flight computer can be used to calculate ground speed, estimated fuel burn and updated estimated time of arrival. They are used during flight planning (on the ground before takeoff) to aid in calculating fuel burn, wind correction, time en route, and other items.
#COMPUTER AIR NAVIGATION PROFESSIONAL#
They are mostly used in flight training, but many professional pilots still carry and use flight computers. Sometimes it is called by the make or model name like E6B, CR, CRP-5 or in German, as the Dreieckrechner. A flight computer is a form of circular slide rule used in aviation and one of a very few analog computers in widespread use in the 21st century.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
